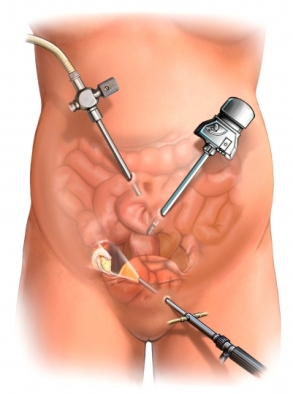
Lap Ovarian cysts
What is Ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the surface of or inside your ovaries. The majority of ovarian cysts are benign, asymptomatic and resolve on their own without medical treatment, while some others may present uncomfortable symptoms that affect your quality of life. Rarely, some ovarian cysts may become malignant (cancerous). Ovarian cysts are common in women who experience regular periods since small cysts can develop naturally as part of the menstrual cycle. Those that develop as a result of regular ovulation are referred to as functional ovarian cysts and cause no symptoms.
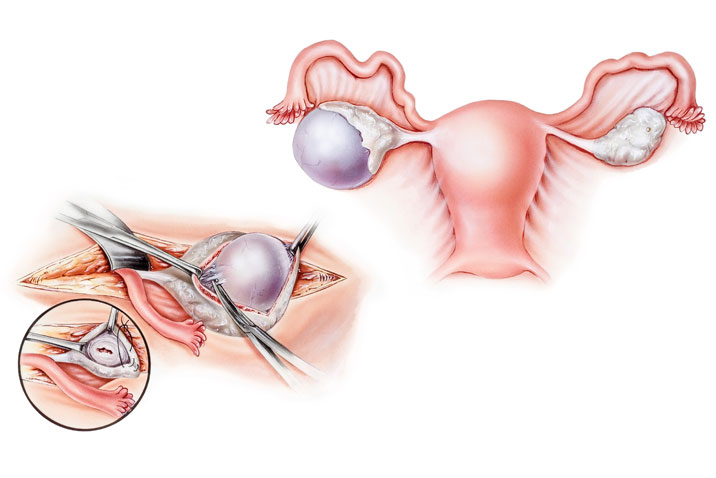
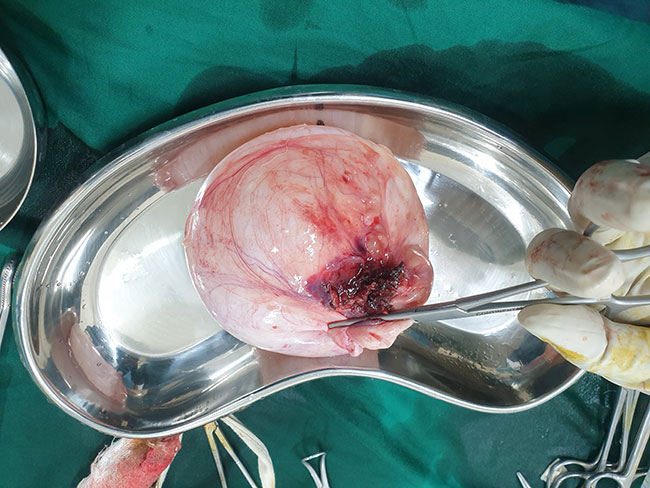
Ovarian cyst
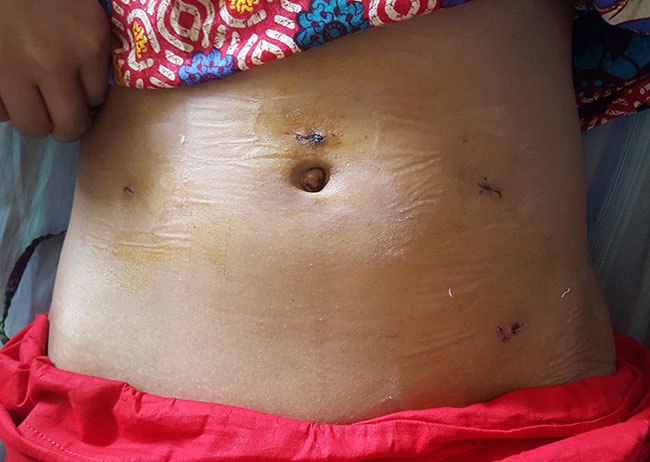
Post Operative view
Dr. Tamjeed Alam is Committed to Provide Personalised, Comprehensive & Holistic Care for You
Reasons for Procedure
An ovarian cyst may need to be removed if it is:
- Causing pain
- Suspected of being cancerous
- Large—more than 2.5 inches in diameter
- Solid
Things that may raise the risk of problems are:
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol
- Chronic diseases, such as diabetes or obesity
- Pregnancy
- Prior abdominal surgery
Possible Complications
Problems are rare, but all procedures have some risk. The doctor will go over some problems that could happen, such as:
- Excess bleeding
- Problems from anesthesia, such as wheezing or sore throat
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Damage to other organs
- Cyst returns after it is removed
- Need for removal of one or both ovaries
Infertility
Dr. Tamjeed Alam is Committed to Provide Personalised, Comprehensive & Holistic Care for You
Description of the Procedure
A small incision will be made just below the navel. Next, a laparoscope will be inserted. This is a thin tube with a camera on the end. Carbon dioxide gas will be pumped into the abdomen to allow the doctor to view the organs better. The laparoscope will be used to locate the cyst. When it is found, one or two more incisions will be made. Small tools will be inserted through them. The cyst wil be removed. Tissue may be removed for testing. If cancer is found, both ovaries may need to be removed. The instruments will be removed. The incision area will be closed with stitches or staples. Bandages will be placed over the area.
The doctor may need to switch to open surgery if the procedure cannot be done laparoscopically. During an open surgery, a larger incision will be made in the abdomen to do the surgery.